A Guide to Thermocouple Wires and Cables
The application of thermocouples ranges from home appliances to industrial processes for power generation, furnace monitoring and control, food and beverage processing, and many more. Thermocouple wires and cables are a significant part of a thermocouple system, available in various forms and types based on usage.
We define thermocouple wires based on their alloy combination, such as chromel, platinum, constantan, and alumnel, working on different temperature ranges with specific functionalities. Insulation and color coding provides extra protection to these wires and are available for specific applications.
Gloster Cables manufactures different thermocouple wire types with various alloy combinations to meet your specific requirement.
What Are Thermocouple Wires and How do They Differ from Copper Wires?

Thermocouples are sophisticated devices that help measure temperature for various applications like kilns, cold storage, diesel engine, etc. And the critical nature of these devices helps avoid incorrect temperature readings. They demand high-quality wiring, i.e., thermocouple wires and cables.
Thermocouple wires get used for creating thermocouple probes for sensing temperature- using the point of cold junction compensation. Other styles in which thermocouples get manufactured are thermocouple probes with connectors, transition joint thermocouple probes, infrared thermocouples, bare wire thermocouples, or just thermocouple wire.
Thermocouple Probes vs Thermocouple Wire
A temperature sensor measures only its temperature. The selection of a thermocouple probe or thermocouple wire depends on how best to get the thermocouple junction to the process temperature we are trying to measure.
We want to measure the temperature of a fluid- in an enclosed or partially enclosed pipe or container. Then, a wire-style sensor may be fine- if the fluid does not attack insulation or conducting material, is at rest, and the temperature is within the material's capability. But if the fluid is corrosive, at high temperature, high pressure, or flowing through a pipe, then, probe style sensor is the proper selection.
Difference Between Electrical Wire and Thermocouple Wires
Let us see how thermocouple wires differ from normal electrical or copper wires.

Thermocouple wires use a few standardized alloys like chromel, alumel, constantan, and platinum, whereas electrical wires mostly use copper as their conductor

Thermocouple wire material focuses on EMF generation related to temperature and measurement accuracy, i.e., limits of error. And electrical wire concern is about current capacity.

Electrical wires are for carrying current, communication signals, and activating process controls, but thermocouple wires application is for measuring temperature.
Thermocouple Wire Parts and Types of Thermocouples
A thermocouple wire consists of different parts and is primarily divided into a measuring junction, reference junction, and extension wire. Here is a detailed view of each part.
Measuring Junction
A measuring junction is the ‘hot-end’ of a thermocouple, where the two wires meet, and the temperature gets measured. There are three kinds of measuring junctions.
 Exposed Junction
Exposed Junction
In an exposed junction, there is no protection for the wire ends, which get rusted and damaged over time.
 Grounded Junction
Grounded Junction
A metal sheath, usually stainless steel, covers the wires in a grounded junction. The design is more stable and long-lasting compared to the exposed junction.
 Ungrounded Junction
Ungrounded Junction
In an ungrounded junction, the sheath is not connected electrically to the wires, and the design is less susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
 Reference Junction
Reference Junction
The other side of the thermocouple, i.e., the cold junction, is known as the reference junction. It is essential to read the wire temperature at rest for an accurate thermocouple readout. This junction is often built into the display instrument and is difficult for users to see.
 Extension Wire
Extension Wire
Thermocouples get placed in extremely hot or cold temperatures, so the temperature reader placed at a distance from the measuring junction ensures the accuracy of temperature readout by using an extension wire. Extension wires are insulated and never calibrated above 240 degrees Celsius to avoid voltage getting affected by other environmental factors.
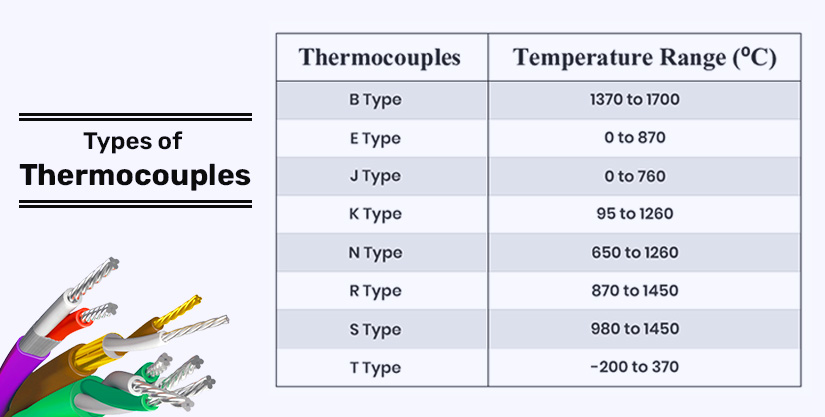
Types of Thermocouples
The standardized alloys used for thermocouple wires give each alloy wire a unique name and have special usage. These alloy wire pairs get referred to by a code name. Listed below are types of thermocouple wires combinations formed using these alloys.
 Type K Thermocouple
Type K Thermocouple
The alloy combination of type K is chromel and alumel, with a temperature range of 0 to 1260 degree Celsius. The thermocouple gets mainly used above 538 degrees Celsius for continuous oxidizing or a neutral atmosphere. And it fails when subjected to Sulphur.
 Type J Thermocouple
Type J Thermocouple
Type J thermocouple has an alloy combination of Iron and Constantan and a temperature range of 0 to 360 degree Celsius. It is suitable for vacuum, reducing or inert atmospheres, and oxidizing atmospheres with reduced life. As Iron oxidizes rapidly above 538 degrees Celsius, only heavy gauge wire is preferable for higher-temperature applications.
 Type T Thermocouple
Type T Thermocouple
With an alloy combination of copper and constantan, Type T thermocouple gets used in oxidizing, reducing, or inert atmosphere, as well as vacuum conditions. They are resistant to corrosion in a moist atmosphere and can work in a temperature range of -200 to 370 °C.
 Type E Thermocouple
Type E Thermocouple
Type E gets formed using chromel and constantan and works under a temperature range of 0 to 870 °C. These thermocouples get recommended for continuously oxidizing or inert atmosphere. They have the highest thermoelectric output of common calibrations and no established sub-limits of error.
 Type N Thermocouple
Type N Thermocouple
Type N has an alloy combination of Nicrosil and Nisil, performing under temperatures 0 to 1260 degree Celsius. We can use Type N with Type K when Type K elements have shorter life and stability problems due to oxidation and the development of green rot.
 Type S and Type R Thermocouples
Type S and Type R Thermocouples
Type S has an alloy combination of Platinum and Platinum with 10% Rhodium, and Type R has Platinum and Platinum with 13% Rhodium. These thermocouples are very similar and have a working temperature range of 538 to 1481 °C. They must get protected with a non-metallic protection tube and ceramic insulators.
 Type B Thermocouple
Type B Thermocouple
The alloy combination of Type B is Platinum (6% Rhodium) and Platinum (30% Rhodium). Type B is similar to Type S and R, but the output power is low and is less susceptible to grain growth and drift.
How Thermocouple Wires Work
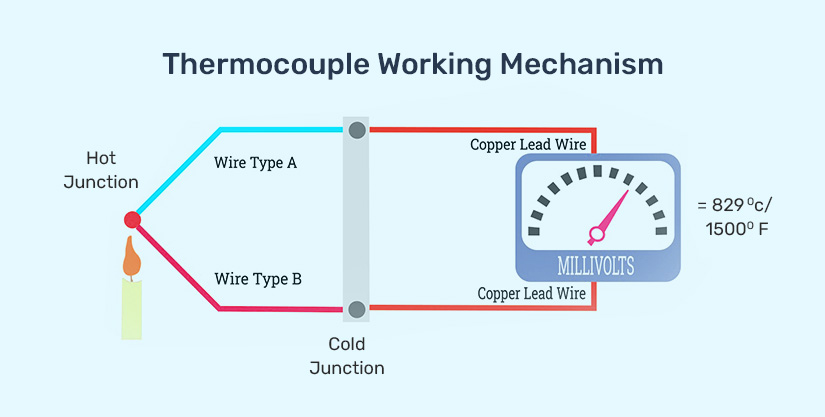
A thermocouple includes two dissimilar metal wires forming together a temperature measurement junction. Through heating the connection point of both metals, a thermoelectric current gets created, known as the Seebeck current. As the heat transfers from the hot end to the cold end, the electrons within the metals create electricity.
For the proper functioning of a thermocouple, one metal should get positively charged and another negatively charged. For example, a positive charge copper in one wire and a negatively charged nickel in another.
A few other factors we need to include for the proper working of the thermocouple system are insulated thermocouple wires and wires length.
Identification of Insulated Thermocouple Wires
The insulated thermocouple wires get color-coded for identification. For example, according to standard guidelines, the negative Lead in the insulated thermocouple is red. The positive Lead has the color of the thermocouple and the overall color of the insulated extension graded wire. And the outer jacket of thermocouple-grade wire is typically brown.
Maximum Length of Thermocouple Wires
The maximum length of thermocouple wires depends on several factors, and the two main factors are total loop resistance and preventing electrical noise from getting into the signal. As each thermocouple wire gets made from different materials, the resistance varies based on the wire type, diameter, and length.
Choose an Appropriate Thermocouple Wire Based on Your Specific Application
The selection of an appropriate thermocouple ensures the accuracy, stability, and precision of a thermocouple system. As leading wires and cable manufacturer, Gloster Cables manufactures a wide range of thermocouple wires and cables of different types and insulation. The thermocouple wires by Gloster adhere to recommended guidelines and standards for high-quality production.
CONTACT US