The Importance of Shielded Cables and Wiring
Industrial applications such as factory floors usually face electrically noisy environments leading to electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) disrupts the proper operation of other equipment on the factory floor. EMI disturbance can reduce the performance of a circuit and even cease its functioning.
In such industrial settings, it is imperative to use shielded cables to reduce EMI and its impact. Shielded cables can reduce the volume and intensity of electrical noise and minimize electromagnetic radiation. Foil and braided shielded cables are the two most common types of shielded cables used for industrial purposes. The selection of shielded cables depends on the industrial setting and work environment.
Understanding the Need for Shielded Cables and their Usage

In heavy processing plants, steel mills, and foundries, there is numerous noise source, such as electrolytic processes, heavy motors, generators, and relay controls. Switching heavy loads, inductive heaters, large transformers, and all can conduct and radiate a high level of electromagnetic interference. And Placing signal cables close to power cables can allow power line noise to couple onto the signal lines.
A cable can act as the primary source to transfer EMI, as a source and receiver. As a source, it can either conduct noise to other equipment or act as an antenna radiating noise. And as a receiver, the cable can pick up EMI radiation from another source.
Thus, shielding is required to protect the cables from EMI and noise effects. Shielded cables are electrical cables containing insulating conductors encased in a standard conductive layer. The shields can get made from braided copper, spiral copper tape, or any conducting polymer.
Shielded cables are thicker and more rigid than unshielded cables and help to protect data getting transferred from the cable due to degradation by EMI exposure. The shields surround the inner signal or power-carrying conductors and can act as EMIs in two ways. It can reflect the energy and noise and conduct it to the ground. However, some energy still passes through the shield, but shields are highly attenuated and does not cause interference.
Shielded cables are thicker and more rigid than unshielded cables and help to protect data getting transferred from the cable due to degradation by EMI exposure. The shields surround the inner signal or power-carrying conductors and can act as EMIs in two ways. It can reflect the energy and noise and conduct it to the ground. However, some energy still passes through the shield, but shields are highly attenuated and does not cause interference.
The shielding in these cables helps reduce the volume and intensity of electrical noise. It lowers the effect on signals and transmission, reducing electromagnetic radiation.
Types of Shielded Cables and Their Application
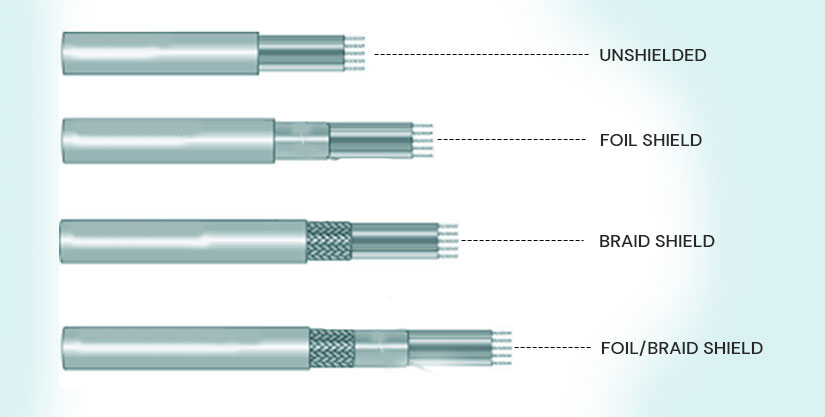
Shielded cables come with various types and degrees of shielding, offering several degrees of shielding effectiveness. The type and amount of shielding depend on factors like the electrical environment of the cable, cable cost, cable diameter, weight, and flexibility.
Served shields, braided shields, braided coax shields, foil shields, and solid shielding are a few types of shielding.
Served Shields
Served Shields are the most flexible shielded cables. They are spiral wound groups of small-gauge wire strands surrounding the conductor insulation. These shields are easy to unwind and terminate but are relatively inductive due to shields coiled around the cable. Served shields are soldered or crimped to a lug or termination post.
Braided Shields
Braids formed using a group of small gauge wires called ‘carriers.’ The braids get laid side by side like a ribbon multipath conductor. Braided shields are woven over and under one another from a tight and flexible wire cylinder. These braids can also get formed using solid ribbons of conducting materials as a strip braid, providing a uniform inner surface to a coaxial conductor and making a very effective EMI barrier at high frequencies when combined with other shield designs.
Braids provide 70 percent to 95 percent coverage to the conductor and allow small gaps in coverage. The braid is more effective as a shield and has more bulk for conducting noise, as copper has higher conductivity than aluminum. However, braids add cost and size to the cable.
Braided Coax Shields
Braided coax shields follow termination in the field through crimping or clamping. It also gets soldered or terminated with a heat-shrink shield pigtail for aircraft wiring harnesses.
Foil Shields
Foil shielding consists of metalized flexible plastic wrappers such as Mylar, polyimide, etc., spiraled around the conductors. It uses a thin layer of aluminum attached to a carrier like polyester for adding strength and ruggedness.
Unlike braid shields, it provides 100 percent coverage of the conductor. The metalized layer is very thin-around .0003 inches, making it harder to work with when applying a connector.
The resistance of foil shields is far higher than other shields and provides the best EMI protection when combined with braided shields. The drain wire gets used to terminate and ground the shield rather than attempting to ground the entire shield.
Solid Shielding
Solid shielding uses a copper or aluminum metal tube (rigid or semi-rigid) surrounding the dielectric and center conductor. It provides 100 percent coverage and low resistance. The shield coverage depends on design and quality level, ranking from poor to perfect. The degree of perfection depends on the frequencies of concern and the noise susceptibility of the circuit. Solid shields are usually soldered or clamped.
Some applications of solid shielded types include short, fixed coax jumpers inside an instrument or ground-based antenna feed.
The Importance or Effectiveness of Shield
The immunity of a shield to induced noise depends on its effectiveness, irrespective of its construction. And shielding effectiveness is the ratio of incident wave field strength to the allowable field strength, expressed in dB.
Shields functions as reflectors or absorbers of radiated electric or magnetic fields. In high-frequency applications, the surface of the shield is an operative element. The conductivity of the surface or its skin plays an important role in high-frequency applications. It is one of the significant reasons why shielding wires are silver-plated in high-performing cables.
The conductivity of copper helps in good absorption and draining of the interfering signal to the ground. As copper is not as effective as steel in absorbing frequencies below 1 GHz, it acts as an effective shield-if absorption and reflection get considered.
Shields are effective in containing interference as well as providing protection from it. It also reduces the effect of noise that may get induced in neighbouring cables or bundles of wires. Better shielding improves signal integrity and system reliability.
Guidelines for Effective Shielding

Here is a list of a few practical guidelines for effective shielding.

Ensure to use a cable with sufficient shielding-based o application needs. For example, in a moderately noisy environment-a foil shielded cable provides adequate protection. And in noisy environments, prefer braids or foil-braid shield combinations.

Cables that experience frequent flexing should use a spirally wrapped shield rather than a braid. Foil-only shielding can tear the foil due to continuous flexing.

The equipment with which the cable gets connected should be properly grounded. The earth's ground should get used for grounding, wherever possible, as eliminating noise depends on a low resistance path to the ground.

Ensure that the connector offers shielding effectiveness equal to that of the cable.
Shielded Cables - An Ideal Choice for Noisy and EMI Risked Environment
Shielded cables are preferable and suitable for use in noisy and EMI-risked environments. The selection of the appropriate shielded cable depends on the application requirement.
Gloster Cables, a leading wire and cable manufacturing industry, brings various shielded cables based on your application need. The shielded cable manufactured by Gloster helps prevent the effect of EMI on equipment and people in several industrial environments.
CONTACT US