How to Prevent the Degradation of Polymers and Decolouration of Cables
The exposure of wires and cables to the outdoor environment gradually reduces their performance, properties, and life expectancy. The impact of sunlight, humidity, and temperature fluctuations causes loss of mechanical and chemical properties and discoloration of wire polymers.
Today, several sectors demand cables and wires that can resist the degradation of polymers and can perform effectively in an outdoor environment without any mechanical or physical loss of properties. Stability, longevity, and performance is their major concern.
To meet these requirements cable industry provides a range of products for outdoor applications, such as photovoltaic cables, power cables, and medium-voltage cables. These cables undergo several weathering, light fastening, and photodegradation tests to withstand adverse environmental conditions.
Gloster cables provide a range of wires and cables that can perform effectively in an outdoor environment without any loss in performance and properties.
Wire Degradation and factors causing degradation
All modern wires have insulation made of a long chain of molecules called polymers. The exposure of these wires to external environmental conditions such as heat, moisture, physical stress, etc., causes gradual degradation in their insulation ability.
Exposure of wires to elevated temperature or mechanical stress brakes or shortens the bond between polymers. We can identify this by measuring the molecular weight of the insulation. And these shorter chains weaken the insulation causing it to break during mechanical movement.
Another reason for wire degradation is exposure to intense light or high-energy radiation, such as UV rays, X-rays, etc. The process is known as photolysis, where light causes a chemical reaction within the polymer. Parts of polymers break down, and even some insulating materials lead to hazardous gas emissions.
At elevated temperatures, oxidation may cause wire degradation. It affects the insulation material and causes weakening at locations along the polymer. Wire degradation due to UV radiation is called photooxidative degradation. Lightfastness covers the exposure of wires to light, whereas weathering includes factors such as humidity and temperature.
Polymeric Photodegradation of Cables and Measures to Avoid
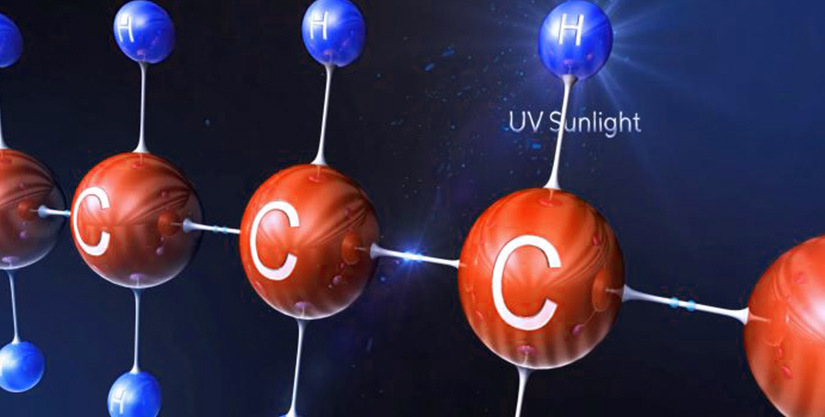
UV radiation causes photooxidative degradation resulting in the breaking of polymer chains, the production of free radicals, and a reduction in molecular weight. It reduces the overall mechanical properties of wires and leads to useless materials. There is a visual degradation of the wires and the brightness of the surface that limits their life. And photodegradation of the chromophore groups of pigments affects the cable's final color.
The strategies used for mitigating the impact of photodegradation in wires and cables are as follows.
UV Filters
The use of UV filters helps absorb ultraviolet light that causes degradation. When sunlight meets UV filters, it reacts like a parasol and prevents the light from entering the polymer and avoiding any damage.
Use of additives
The application of additives like Hindered Amine Light Stabilizer (HALS) reacts to free radicals and block and avoid form polymer chain breakdown. When UV light strikes the polymer and free radicals get generated, HALS helps stop the degradation process of polymers. A synergistic combination of UV filters and HALS also gives good results. We can also use anti-oxidant additives to avoid polymer degradation due to thermal stress.
Application of carbon black
Carbon black absorbs a high rate of ultraviolet radiation and helps stop the photodegradation of polymers. It captures the energy and prevents it from reacting with the polymer. A carbon black with the smallest size is most effective as they present a larger surface to trap solar radiation.
Colour Protection of Cables
There are no additives that can protect the colour of the cable as it does the polymer. Therefore, we can formulate the colour using prepared pigments to withstand outdoor conditions and avoid colour degradation. It is essential to make a correct choice of pigment or combination of lightfast pigments.
The polymers like PVC, HFFR, TPU, XLPE, and EPDM used in cables have different pigment behaviour, and we need to study them to ensure cable colour stability in outdoor conditions.
How to prevent Weathering and Lightfastness in Cables
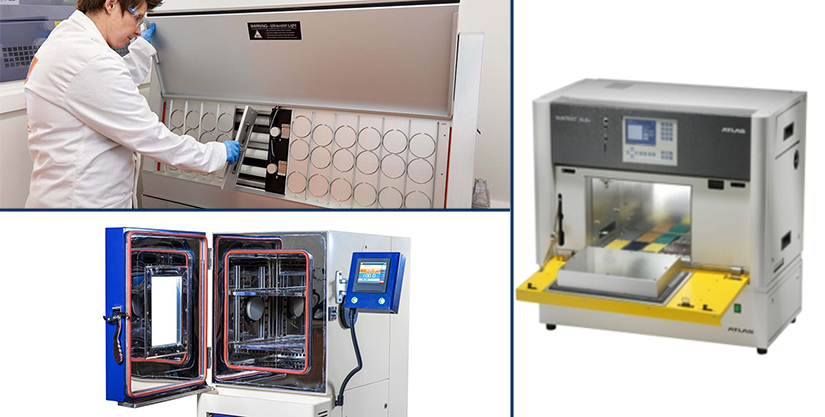

We can measure the behaviour of polymer pigments used in wires and cables with the help of several tests. It helps us to know what kind of behaviour we can expect from outdoor cables and select the pigments accordingly to improve life expectancy. It contributes to the installation of solid cables that are capable of withstanding weathering and lightfastness conditions.
 Humidity Chamber
Humidity Chamber
A humidity chamber is a reliable instrument used to evaluate the environmental limits for weathering of electric cables. The equipment artificially replicates the environmental conditions to which a product or specimen may be exposed. And you can monitor the effects and changes caused due to sudden extreme temperature variations, altitude, moisture, or relative humidity and weathering.
 Accelerated Weathering
Accelerated Weathering
The accelerated weathering technique is the test that fast reproduces the damage that sunlight and moisture cause overtime on outdoor exposed wires. It exposes materials to the alternating cycle of UV light and moisture at controlled and elevated temperatures. The effect of sunlight and dew gets simulated using fluorescent UV lamps and condensing humidity. The resulting performance determines whether a cable can deliver UV stability and performance after aging and weathering.
 Suntest for Critical Pigments
Suntest for Critical Pigments
A better understanding of pigment behaviour in the different types of polymers used in the cable industry is essential to propose pigment formulations that obtain the required colour with excellent colour stability when faced with outdoor conditions. Red and yellow pigments are the most sensitive to light and weather effects.
Suntest is a laboratory apparatus, which under standardized conditions, allows us to make behaviour predictions of these pigments in different polymeric bases and with necessary conditions.
It is essential to carry out these tests with the critical pigments to avoid degradation of the chromophore group of these pigments that results in discoloration of the cables in a much shorter time. And problems may arise related to the repair & control of electrical circuits and data cables in outdoor installations.
Avoid Polymer Degradation and Decolouration to Enhance Ageing and Stability
of Cables

We can prevent polymer degradation and untimely decoloration of wires and cables due to outdoor conditions with the help of proper tests and the use of additives for insulation. Weathering and lightfastness tests ensure the proper-selection of pigment formulation for colour stability and study changes due to humidity and temperature variations.
Gloster Cables manufactures wires and cables considering several outdoor conditions that give these cables chemical, thermal, humid, and mechanical stability. Gloster follows regional standard practices and testing to prevent polymer degradation and decoloration of its wires and cables.
CONTACT US