Underground Cables and Their Classification
Underground cables are slowly rising in demand due to increased urbanization, congested areas, and safety concerns. The advancement in underground cables is gradually broadening its space in high voltage usage from low and middle voltage applications.
There are several categories to classify underground cables, including voltage rating, conductors, construction, insulation, thickness, and installation and laying of cables. For a particular location, underground cables are used based on their voltage rating and other criteria.
Gloster Cables manufactures a range of underground cables using XLPE, PVC, and other insulators for different voltages.
What are Underground Cables?
The use of underground cables is for electrical transmission for places where overhead construction is not practical.
For example, for congested places or urban areas, around factories or plants, crossings of water bodies, etc., where overhead lines get prohibited due to safety and difficulty.
UG cables for suitable for electricity distribution in low and middle voltage systems. With recent advancements, UG cables are now suitable for high power transmission for short and moderate distances.
The structure of an underground cable consists of
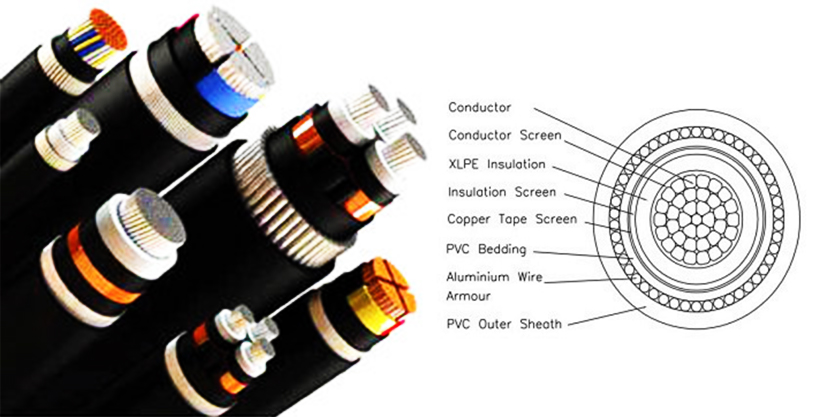
 Stranded Conductor
Stranded Conductor
The number of conductors varies from 1 to 3, made from copper or aluminum. These conductors are stranded to reduce skin effect, proximity effect, and also to maintain flexibility.
 Conductor Screen
Conductor Screen
There is a semi-conducting tape or an extruded layer of semi-conductive compound above the stranded conductor. Mostly used for MV and HV, the conductor screening helps maintain a uniform electric field and minimize electrostatic stress.
 Insulation
Insulation
Based on the voltage, several insulators, like VIR (Vulcanized India Rubber), Impregnated paper, PVC, and XLPE, are used to withstand electrostatic stress.
 Insulation Screen
Insulation Screen
Insulation screens of semi-conductive material are in use for MV and HV lines.
 Metallic Sheath
Metallic Sheath
A metallic sheath is made of aluminum or lead, protecting from moisture and other chemicals that are present in the environment or soil. The sheath is earthed at one end, providing a path for fault and leakage current.
 Bedding
Bedding
A low-grade insulator made of jute or hessian helps protect the metallic sheath from corrosion and any mechanical injury due to armouring.
 Armouring
Armouring
Armouring is steel tape wound around the bedding layer, providing mechanical protection from stresses during installation and operations.
 Serving
Serving
Serving is another layer of insulation using jute, hessian, or a thermosetting compound like PVC to protect the steel from contaminants and agents.
Classification of Underground Cables

The classification of underground cables considers several criteria, from the number of conductors, voltage rating, construction, and insulation to the lying of cables.
Number of Conductors
The underground cables, based on the number of conductors, areA three-core cable is suitable for voltage up to 66 kV.
For higher voltages, three-cored UG cables become bulky.
So, single-core UG cables may get used with some limitations.
Voltage Rating
According to the voltage rating, we can group underground cables as
 Low Tension Cables
Low Tension Cables
These low-tension cables can handle a maximum voltage of 1000 V.
 High Tension Cables
High Tension Cables
A high-tension cable has a voltage handling capacity of 11 kV.
 Super Tension Cables
Super Tension Cables
Super tension cables can operate at a maximum voltage of 33 kV.
 Extra High-Tension Cables
Extra High-Tension Cables
They can handle a maximum voltage of 66 kV.
 Extra Super Voltage Cables
Extra Super Voltage Cables
Extra super voltage cables are preferable for applications with voltage requirements above 132 kV.
Construction
The underground cables based on construction are belted cable, screened cable, and pressure cable.
Belted Cable
In belted cables, the conductors are grouped and bunched together with an insulating paper belt. And each conductor gets insulated with an insulating paper impregnated with a suitable dielectric. The gap between the conductor and insulating paper belt filled with a fibrous dielectric material, such as jute or hessian, provides flexibility and a circular shape.
Then, metallic sheath and armouring cover the jute layer.
The electric field is tangential, and the insulation provided is stressed, resulting in a fall of dielectric strength over time.
Belted cables are not fit above a voltage of 11 kV.
Screened Cable
Screened cables are H-Type, S.L Type, and H.S.L Type cables.
H-Type Cables
The three cores of H-Type cables are individually insulated with paper and covered with a metallic screen. These metallic covers are perforated, allowing the three metallic screens to touch each other. Then, together grouped in a metallic tape made of copper and a lead sheath surrounds them. The metallic cover and sheath get grounded, resulting in radial electric stress not tangential and of lesser magnitude. The metallic cover helps improves heat dissipation.
S.L Type Cables
Unlike H-Type cables, in S.L Type cables, every three cores have its lead sheath, and there is no overall lead sheath. This minimizes the chances of core-to-core breakdown, improving flexibility.
These cables are limited to a voltage of 66 kV.
Since the individual sheath is thinner, any construction defects cause moisture to enter the cable reducing the dielectric strength.
H.S.L Type Cable
These are H-Type and S.L Type combined cables, in which each core gets insulated with impregnated paper and separate lead sheaths.
Pressure Cable
Pressure cables are oil-filled or gas-filled cables.
In Oil filled cables, oil gets circulated under suitable pressure through ducts. Oil supply and pressure get maintained through reservoirs placed at proper distances.
The Gas-filled cables use pressurized gas circulated cables in an air-tight steel pipe. They can carry higher values of load current and operates under higher voltage.
Insulation Type and Thickness
Underground cables are suitable for urban and congested areas where overhead lines are difficult and unsafe to install. Some other benefits of these cables are
Installation and Lying of Cables
Based on the installation and laying of cables, UG cables are named as direct buried, trough, tunnels, and gas-insulated lines. Gas-insulated line construction is safe for cables operating at higher voltages, power, and current. It is used mainly for advanced projects.
Underground Cables as a Better Alternative for Power Supply

Underground cables are suitable for urban and congested areas where overhead lines are difficult and unsafe to install. Some other benefits of these cables are
Gloster Cables as an Underground Cable Provider
Gloster Cables is an established wire and cable service provider. With state-of-the-art infrastructure, the organization manufactures high-quality, robust, and performing wire and cables for power, commercial, industrial, and domestic usage. Gloster Cables manufactures underground cables classified under various categories to meet the power supply demand for different locations.
CONTACT US