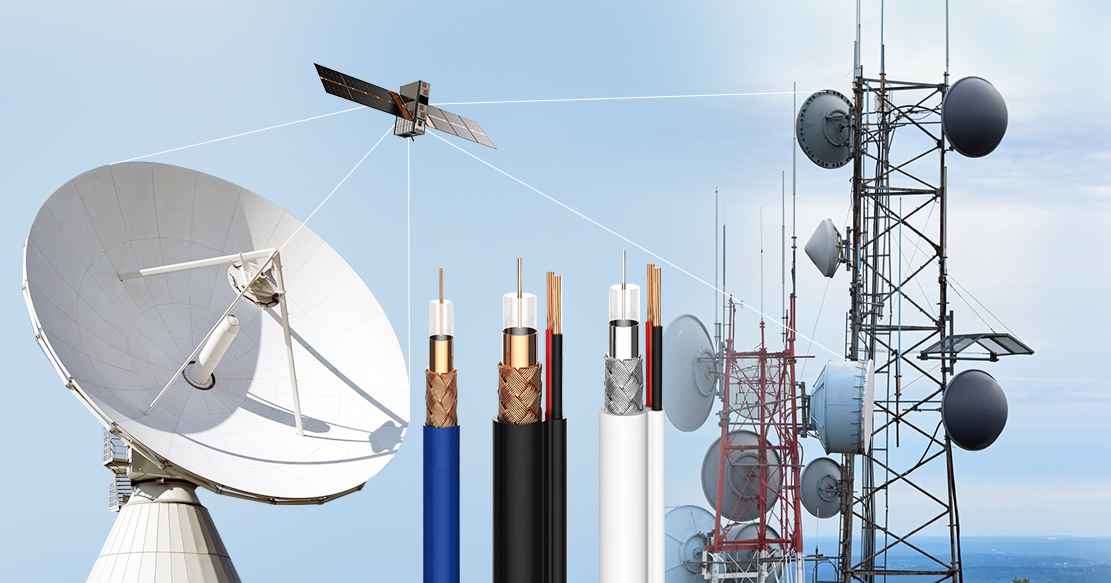
Role of Co-axial Cable in Communication Network
Coaxial cable and its technology have been around since the 20th century for connecting satellite antenna facilities to homes and businesses. Coaxial cables are electrical cables that transmit radio frequency signals from one point to another.
The applications of coaxial cables demand high resistance to EMI and noise, high flexibility, ease of installation, high bandwidth, and others. These cables are available as RG6, RG11, RG59, RG174, RG8 X, and RG 213. In these, RG6, RG11, and RG59 support Telecom projects and civil works.
An Overview of Co-axial Cable
A coaxial cable is an electrical cable- built with a metal shield and other components engineered to block signal interference. The cable consists of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield, and the two get separated by a dielectric insulating material.
Some coaxial cables have a protective outer sheath or jacketing. The cable was termed 'coaxial' because the inner conductor and the outer shield share a geometric axis.
Primarily, Cable TV companies use coaxial cables for connecting satellite antenna facilities to customer homes and facilities. Several Telephone companies use these cables to connect central offices to telephone poles near customers. Twisted pair cabling of coax cables has supplanted the cable use as an Ethernet connectivity medium in enterprises and data centres.
Design of a Co-axial Cable and How it Works

Coaxial cable design affects its physical size, frequency, performance, attenuation, power handling capabilities, flexibility, strength, and cost. Coaxial cable design consists of the following parts.
 Centre Conductor
Centre Conductor
The centre conductor can be solid or stranded. A stranded conductor is more flexible, and a silver-plated conductor has better high-frequency performance. In the cable TV industry, copper-plated steel wire is preferable for the inner conductor. The conductor helps transmit data and video.
 Insulator
Insulator
The insulator surrounds the centre conductor, made of solid plastic, foam plastic, or air spacers supporting the inner wire. The properties of the dielectric insulator help determine a few electrical properties of the cable. Insulation materials like Solid Polyethylene and Solid Teflon are common in lower-loss and plenum-rated cables. Some coaxial cables use air and spacers to keep the inner conductor from touching the shield.
 Braided Mesh
Braided Mesh
Braided mesh made from copper wire forms the shield and protects it from electromagnetic interference. It also makes the cable flexible. A few cables have double-layer shielding, such as a quad-shield, a four-alternating layer of foil, and a braid. The braids can be silver-plated.
 Protective Plastic Layer
Protective Plastic Layer
The external layer of the cable is a plastic coating that protects the internal layer from damage.
Working of a Co-axial Cable
A coaxial cable carries data in the centre conductor, and surrounding layers of the shielding help stop any signal loss, also known as attenuation loss. The surrounding layers help reduce EMI.
The first layer of insulation (called dielectric) provides a distance between the core conductor and outer layers. The next layer, collectively referred to- shields, keeps electrical impulses and radio transmission away.
The electromagnetic field carrying the signal exists only in the space between inner and outer conductors. Therefore, we can install these cables next to metal objects without any power loss. The transmission speed of a coaxial cable is 10Mbps, offering 80 times more transmission capacity than twisted pair cables.
Types of Co-axial Cables and Role in Supporting Communication Network

There are numerous coaxial cables, some of which are
 Hardline Coaxial Cable
Hardline Coaxial Cable
Hardline coaxial cables have round copper tubing and use metals such as aluminum or copper for shielding. We use these cables to connect a transmitter to an antenna.
 Flexible Coaxial Cable
Flexible Coaxial Cable
Flexible coaxial cable has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible polymer. It gives flexibility to the cable.
 Semi-rigid Coaxial Cable
Semi-rigid Coaxial Cable
This cable uses a solid copper outer sheath with a dielectric of Polytetrafluoroethylene.
 Formable Coaxial Cable
Formable Coaxial Cable
Formable coaxial cable is an alternative to semi-rigid cable. These cables use a flexible metal sheath instead of a rigid copper outer sheath.
 Twin axial Cable
Twin axial Cable
These cables have two central conductors in the core and a single outer core and dielectric. They are suitable for low-frequency digital and video transmission.
 Triaxial Cable
Triaxial Cable
Triaxial cable is also known as Triax. It has an additional copper braid, compared to coaxial cable, which protects it from noise and acts as a shield. These cables offer more bandwidth.
 Rigid Coaxial Cable
Rigid Coaxial Cable
Rigid coaxial cable is made with two copper tubes supported at cable ends and at fixed intervals across the cable length, using PTFE supports or disk insulators. These cables cannot be bent and used for TV and FM broadcasting.
 Radiating Cable
Radiating Cable
Radiating cables include many components similar to hardline cables but with tuned slots in the shielding matched to the RF wavelength at which the cable operates. It is applicable in elevators, military equipment, and underground tunnels.
Role of RG6, RG11 and RG59 in Communication Network
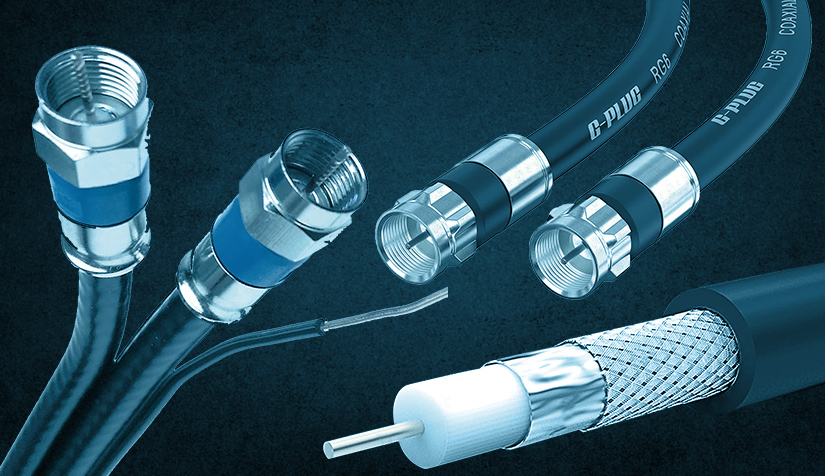
RG coaxial cables are applicable for effective transmission solutions for Telecom systems, such as Satellite communication, marine, mobile communication, AM, FM, Rada communication systems, etc.
RG6
RG-6/U is a common type of coaxial cable used for various residential and commercial applications. RG6 Cable has an 8 AWG center conductor and 75-ohm characteristic impedance. CATV (Cable television) distribution coax is the most recognized RG-6, used to route cable television signals to and within homes. RG6 cables application is in professional video applications and carries baseband analog video signals or serial digital interface (SDI) signals.
RG11
RG11 coaxial cables are thick and used for special and long-distance signal purposes. These cables support Wide broadband with far signal transmission distance and are applicable as the main cable line in transmitting observing camera data, cable television, etc.
RG59
RG59 cables have intertwined multi-small fibers that make them flexible. The common application of RG59 is for CCTV applications and other audio video applications requiring a 75-ohm cable. They are suitable for analog TV aerials, component video cables, home theatres, and short and medium-length connection cables between digital cable, and satellite receivers.
Gloster’s High-Performing and Optimum-Quality Coax Cables
Gloster Cables, a leading wire and cable manufacturer, provides high-quality RG6, RG11, and RG59 cables for an effective transmission solution for Telecom systems such as satellite communication, mobile communication, marine, etc. The cables manufactured at Gloster support high bandwidth and multiple channels and provide better defense against noise and EMI. Gloster's stringent quality check and manufacturing policy make the coax cables more reliable and durable.
CONTACT US