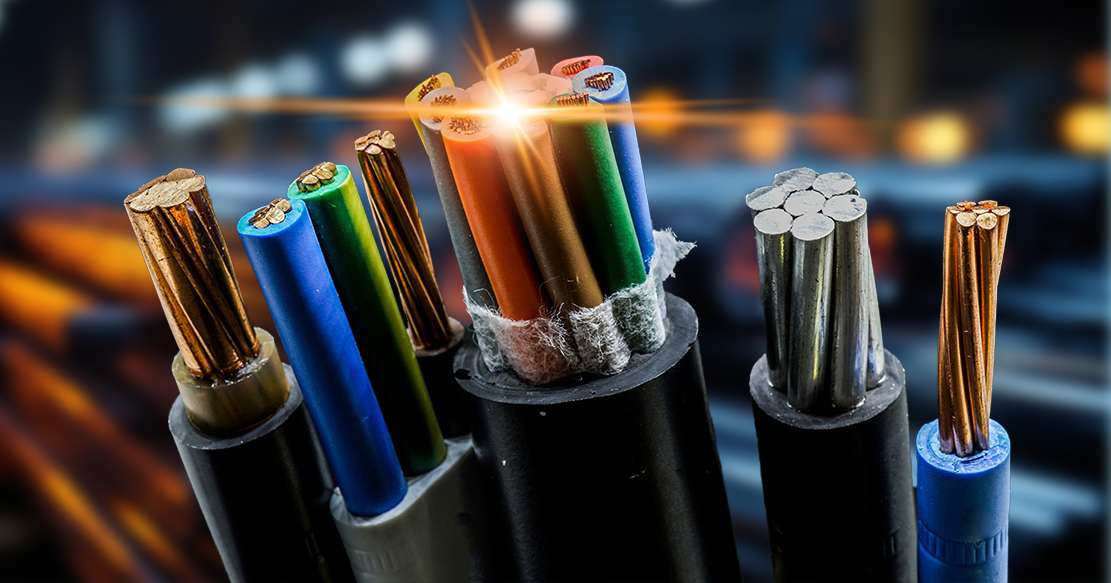
Conductors: Materials, Coating, and Class of Conductors for Wires and Cables
Conductors are the primary component of wire and cables. They play a significant role in defining the wires and cables efficiency, conductivity, and safety of electrical transmission.
The fundamentals that decide the efficiency and usage of a conductor are its material type, conductor coating, and specification of conductor class. Conductors of different materials have different properties and conductivity levels. Coating of conductors using metals like silver, nickel, etc., enhances their corrosion resistivity, conductivity, safety, and performance.
Gloster Cables manufactures cables using various conductors, like copper and aluminum, depending on the application and performance of the cable.
Conductors and Their Importance in Wires and Cables
Conductors are the materials that conduct electricity. They have substances called electrons and electrical charge carriers. When we apply voltage, these electrons make it easy for electricity to pass through. Metals are the good conductor of electricity, such as copper, iron, silver, and aluminum.
At the center of each wire and cable is a conductor, an electrical highway for carrying power or data from one point to another. Cables insulated with coatings help prevent electrical leakage and protect against electrical shock. Cables use different metals as conductors based on their properties and conductivity levels. Wires and cable manufacturers get various options for selecting an electrical conductor. It depends on wires and cable application and their optimal performance.
Different Types of Materials Used for Conductor
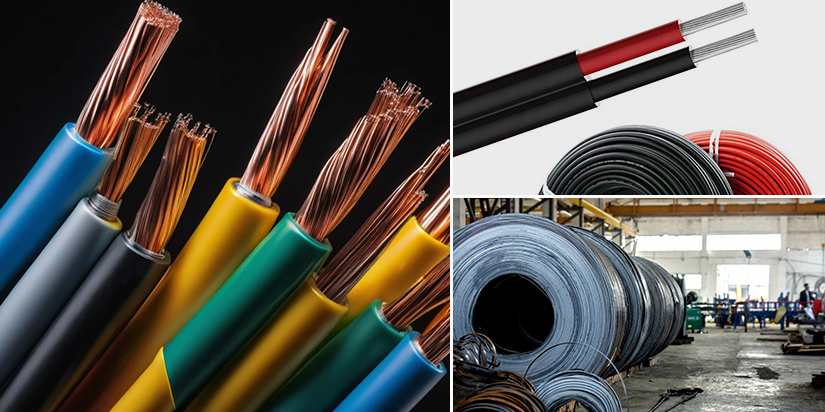

The most frequently utilized materials for conductors in electrical wiring include copper, aluminum, high-strength alloys, and steel.
 Copper
Copper
Copper is a highly versatile and relatively inexpensive material, making it the most widely used conductor material in everything from home wiring to power transmission networks. Copper provides exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, malleability, and solderability. It has a high melting point and high resistance to corrosion and wear. Wires and cables using bare copper conductors allow efficient energy transfer and greater signal integrity. And tinned and or silver-coated copper can provide even more performance.
 Aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminum conductors are lightweight, affordable, and used in various applications. The light- weightiness of aluminum makes it a popular choice for long-distance power transmission. It helps reduce expenses in large-scale electrical systems. However, it is prone to oxidation and corrosion, which increases resistance and potential reliability issues over time.
 Steel
Steel
The steel used as a conductor delivers exceptional mechanical strength. It often gets used in medical lead wires and cables due to its strength and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel plated with other metals like gold or copper gives more conductivity. Copper-covered steel conductors are preferable for grounding purposes, line tracing to locate underground utilities, telephone drop wire cables, and inner conductors of coaxial cables.
 High-Strength Metal Alloys
High-Strength Metal Alloys
The combination of two or metallic elements improves limited strength or corrosion resistance. A few alloys are cadmium copper, chromium copper, cadmium-chromium copper, and zirconium copper. Copper alloy conductors feature high tensile strength and great flex life and are preferable for various electrical applications.
Conductor Coating and Their Types
Uncoated conductors like copper are highly conductive. They are ideal for applications in limited extreme temperatures, moisture, and external threats. Conductor coating enhances the performance and durability of conductors. A few types of conductor coating are
 Silver-Plated Conductor
Silver-Plated Conductor
Silver coating over conductors improves conductivity, performs in higher frequencies, and facilitates a wide range of operating temperatures. Silver-coated conductor wires and cables are in demand in aerospace applications.
 Nickel-Plated Conductor
Nickel-Plated Conductor
A thick nickel plating of a conductor enables the wire to withstand a temperature range of up to 750°C. It enhances corrosion resistance and durability. In the case of solder wicking as a concern, nickel plating is preferable to silver coating.
 Tinned Conductor
Tinned Conductor
Tinning is a process to melt tinned solder around a wire strand to improve protection against oxidation and corrosion. Various types of tinning include
 Tinned
Tinned
Individual conductor strands are tin-coated with basic tinning under UL, CSA, ASTM, and Mil- Spec standards.
 Heavy-Tinned
Heavy-Tinned
A much thicker coating of tin gets applied to the conductor. Its use is common in high-frequency induction heaters as it can bond on stripped areas while the rest of the cable remains flexible.
 Prefused
Prefused
In prefused tinning, heavy tinned copper strands get twisted and fused along their entire length.
 Overcoat
Overcoat
It covers tinned, twisted copper strands with an overall coating of tin.
 TopCoat
TopCoat
In topcoat tinning, bare copper strands are twisted together and given an overall tin coating.
Different Class of Conductors and Their Application

The classification of Conductors into different classes depends on their purpose of use.
 Class 1: Solid Conductor
Class 1: Solid Conductor
Solid conductors are manufactured as bare or metal coated from single wire and in the range of 0.5-16 mm-square for the intended use.
Types of Cables Using Class 1 Conductor
The cables with class 1 conductor are HO5V-U, HO7V-U, HO5Z1-U,HO7Z1-U with conductor cross-section <16mm2 of NVV, YVV,YVCV,N2XRH, YXV, etc.
 Class 2: Stranded Conductors
Class 2: Stranded Conductors
Stranded conductors are bare or metal-coated circular, compacted circular, or sectoral forms for the intended use. The range of circular forms is between 0.5-1200 mm square, compacted 16- 1200 m square, and sectoral forms 35-400 mm square.
Type of Cable Using Class 5 Conductor
Neoprene cables, solar cables, and KEYFLEX cables use class 5 conductors.
 Class 6: Conductors with flexibility more than Class 5
Class 6: Conductors with flexibility more than Class 5
Class 6 conductors are extremely flexible and extra multi-stranded.
Type of Cable using Class 6 Conductor
Welding cables use class 6 conductors because of their flexibility.
Gloster Cables Choose Perfect Conductors for Their Cables to Optimize Performance
Gloster Cables has been a trusted wire and cable manufacturer for over 25 years. The organization brings a wide range of electrical and power cables for domestic and industrial usage. The experts at Gloster use perfect conductors based on their material, coating, and class to meet the usage requirement of wires and cables and optimize their performance.
CONTACT US