High Voltage Wires and Cables: The Industrial Usage and Rising Demand
Cables are used for electric power transmission and subsequently designed to operate on a specific range of voltage levels. The electric cable we use for transmitting 450-750V of electricity does not work for high voltages such as 3-220KV. We require a special power cable that ensures our safety and complies with all the safety standards for reliable transmission for transmitting high voltages.
High Voltage (HV) cables consist of conductor, insulation for underground and under the water, and cable and joints for controlling HV impact and robust and sustainable insulation. HV cables are structurally different from normal cables because of the additional internal layer in the insulation jacket, which also helps control the electrical flow around the conductor and reduces power loss during long-range transmission.
Compared to normal cables, HV cables are highly efficient in power transmission and consequently can run as overhead cables and buried cables in industries, power plants, and submarines. The application of HV cables prevents the contact of objects or living beings with a high-voltage conductor.
A Historical Perspective of High-Voltage Cables
The HV cables require a robust insulation system to hold the electrical stress and perform at 2KV and above voltage.
In 1916, Martin Hochstadter patented a technique of conductive shield around each insulator conductor to equalize the electrical stress, and the shielded cable was named an H-type cable. When grounding such cables, you can connect the shields of the cable at one or both ends of the cable. Based on the length of the circuit, you can also ground the splices in the middle of the cable.
Later in 1960, solid dielectric extruded cables insulated with EPR & XLPE polymeric insulation got introduced that captured the market. EPR insulation is generally used in 4kv to 34kv cables, whereas XLPE insulation works for all the cables above 600v.
PILC cables or paper insulated lead cover cables introduced in 1887 slowly lost the market because of the high level of craftsmanship. The modern HV cables use polymers like Polyethylene, Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) as insulation.
Specifications of High-Voltage Wires and Cables
The structure of HV cables depends on their working and function. The components of HV cables are:
Conductor
The conductor carries the current and requires low resistance for reducing power loss. ACSR, Aluminium conductor steel reinforced, is the most common conductor in use because of its flexibility, weight, and susceptibility to corrosion. Though for low voltages and grounding, copper is preferable over ACSR.
Conductor Shield or Screen
Cables need a conductor shield to provide a smooth interface between the conductor and the insulation. The absence of a conductor shield can concentrate the electric field lines, further creating high-stress points at the conductor/insulation interface.
The shield gets made with semiconducting materials or materials with high dialectic constant. In the case of extruded cables, this shielding layer is extruded directly over the conductor and bonded with the insulation layer.
Cable Insulation
Insulation maintains the voltage between the conductor and ground and should be operating at the required temperature and electrical stress. The laminar insulation cables are PPL paper polypropylene insulated for low loss, whereas extruded cables are XLPE and EPR insulated. Select PPL cables for large sizes and voltages above 275 kV.
Insulation Shield or Screen
The use of an insulation shield keeps the voltage and stress within the insulation. Also, prevent the formation of high-stress points on the outside surface of the insulation. Shields are metallic or non-metallic.
Metallic Shield
Another layer is the metallic shield, and this insulation layer is usually copper, aluminum, lead, or stainless steel. The cables transmitting current more than 5KV require a metallic shield, and this metallic component carries leakage current, short-circuit current, and neutral current to the ground in a few cases.
Jacket
The jacket is the outermost layer of the cable and mechanically protects the insulation and conductor of the cable from physical forces and chemical deterioration. In standard cases, the outer jacket gets built from materials like PE(Polyethylene), PVC (Polyvinyl chloride), and PP(Polypropylene).
The layers of insulation depend on the level of voltage a cable would be transmitting. For example, Power cables generally contain at least one or more conductors, appropriate insulation, and a jacket for safety. Power distribution cables of 100kv get insulated with oil and paper, and aluminum and lead covering.
Sourcing Raw Materials for High-Voltage Cables
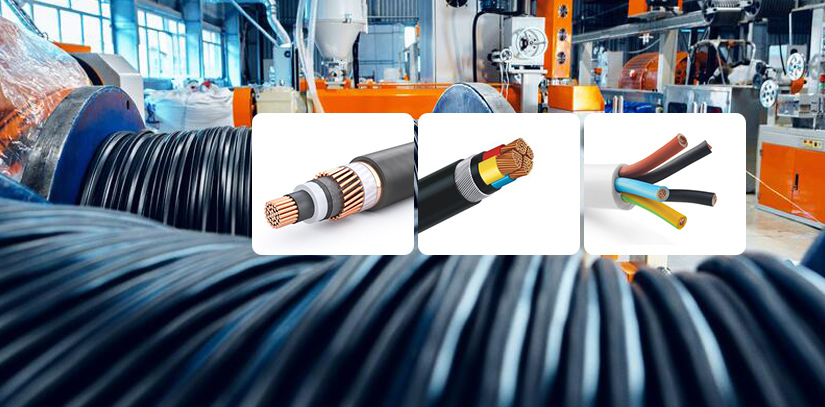

The raw materials used for making HV cables are copper, aluminum, PVC, and XLPE compounds.
Copper Wires
Copper wire uses commonly uses electrolytic copper. Low-oxygen copper is made by following continuous casting and rolling process, while oxygen-free copper requires an up-drawing method in making.
Aluminum Wire
Aluminum is annealed and softened while making wires. But for making cables, you do not need to soften aluminum.
Aluminum must reach an electrical resistivity of 0.0282649mm2/m and a specific gravity of 2.703g/cm3 for making wires and cables.
PVC
For PVC plastic, you can mix polyvinyl chloride resin with compounding agents like antioxidants, fillers, brighteners, flame retardants, etc. The PVC materials have a density of 1.38~1.46g/m3, excellent mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, weather resistance, electrical insulation, and easy processing.
XLPE
These days, the two main categories of XLPE cables in use are silane cross-linking material and cross-linked polyethylene material combined with dicumyl peroxide. Cross-linked polyethylene is for insulating HV cables. The higher the insulation withstand voltage higher should be the purity.
Demand and Market Size of HV Cables
The global HV cable market is growing highly because of the increasing demand in the selected segment such as submarine and underground. As to a survey, ‘HV cable market by installation and end-user: Global opportunity analysis and industry forecast 2020-2027’, the HV cable market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6 percent globally.
Also, the market size of HV cables is forecasted to reach $ 23.4 billion in 2027 from $14.6 billion in 2019.
The growing infrastructure is rising demand for power cables in commercial and residential buildings and expanding the market size.
We are observing a significant increase in HV cable demand in industrial and renewable energy segments such as power utilities, oil & gas, hydro, wind, etc. Asia-Pacific is the fastest growing and revenue-generating region.
The Future and the Gloster Cables
Gloster Cables is a well-known name in the industrial and domestic cables manufacturing and supply domain. The industry is catering to the rising demand for HV cables for various segments, from industrial, commercial, and residential to others.
The organization manufactures high-quality HV XLPE cables with different metallic shields such as Welded Copper Corrugated sheath, welded aluminum corrugated sheath, concentric copper neutrals, etc., adhering to various national and international safety standards.
Gloster Cables lead the competition with a continuous focus on research and development and market awareness. We are marching with our modern and updated infrastructure to meet the rising need for HV cables around the globe with our excellent wires and cable products.
CONTACT US
